Understanding TMS: A Solution for Treatment-Resistant Depression
TMS or transcranial magnetic stimulation affects the brain cells. It can also depolarize the neurons in the cerebrum. The U.S. FDA approved TMS treatments for patients who have depression. Many psychiatrists recommend this method for specific patients. If you want to know when this happens, the following are the conditions.
A diagnosis of MDD
Sadness is usually fleeting. Major depressive disorder (MDD) is intense sadness that persists for long periods. Psychiatrists also refer to MDD as clinical depression. It tends to affect the patient’s behavior, mood, and physical functions. While some seek treatment, others do not.
Those who do seek professional help tend to function better. Methods such as psychotherapy and medications tend to improve and manage depression symptoms. But, some patients seem to be resistant to conventional treatments. This is when the patient develops TRD or treatment-resistant depression.
How MDD patients become TRD patients
There are times when depression does not get any better. Psychotherapy and medications usually ease depression for many depressed patients. Once a patient develops resistance, these treatment methods stop working. There would be signs of improvement for a while, but the symptoms would always come back.
There is no specific way to tell how a depressed patient becomes treatment-resistant. Yet, studies show that gender, health status, and age may put patients more at risk for treatment resistance. For example, seniors and women experience resistance at more elevated rates. The reasons may likely be psychological and biological. The same happens for people who have recurring episodes of depression.
How TMS works for TRD
When there is treatment resistance, psychiatrists often recommend TMS. Before TMS sessions start, the psychiatrist must first check the patient well. The psychiatrist must be diligent and watch out for pseudo TRD. This might be the result of patient nonadherence and misdiagnosis. Pseudo resistance may also rise from taking low doses of antidepressants.
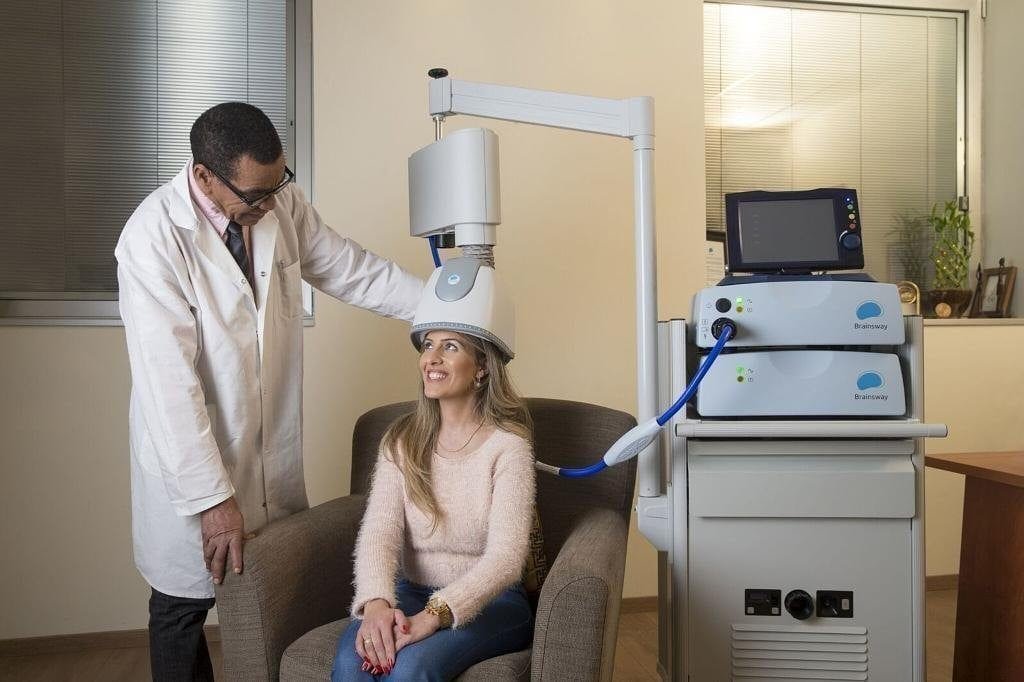
TMS devices target the DLPFC (dorsolateral prefrontal cortex). This area of the brain handles functions like organization and cognitive flexibility. These machines stimulate all the DLPFC’s connecting parts. This action also triggers other sections of the brain that affect mood.
This treatment depends on magnetic waves. That is why there are precautions and restrictions for his approach. Various items, such as medical devices, might interfere with the TMS machines. The patient should remove any piece of jewelry or piercings before the session. Braces and dental fillings are all right. Patients should ask about the allowable materials for dental restorations.
TMS is a non-drug, non-invasive method of treating treatment-resistant depression. There are no adverse effects since there are no medications. The common side effects of TMS are scalp discomfort and slight headaches. Patients can benefit from this method because it is potent, cost-effective, and time-saving.
During the treatment
The patient will go to the treatment facility. The attending doctor will administer the TMS therapy. The healthcare provider will find the right spot on the patient’s head and place a magnetic coil on it. The strength of the magnetic power is similar to a machine used for magnetic resonance imaging. The technician will ask the patient to remove any object that has metal components.
The doctor will adjust the energy and treatment settings during the first session. The coils need to target the prefrontal cortex. Studies show that this area of the brain is linked to depression. The doctor will send quick magnetic pulses to the brain. Knowing the patient’s threshold is possible through the twitching of fingers and hands.
These pulses stimulate the production of serotonin, which regulates mood. The patient will feel some taps and hear some clicks as the coils deliver the pulses. The treatment can take 20 to 50 minutes. There will be no anesthesia, so the patient does not need to recover much after the treatment. The patient can drive home and continue the day’s activities. The doctor can stop the treatment at any point the patient wants to stop.
Possible side effects
TMS can result in mild side effects. Some patients stop having treatments because of them. Others continue once these side effects fade. Below are some of the common side effects a patient may experience after a session:
A patient may suffer from mild hearing problems because of the loud machine noises. Some patients can have temporary hearing loss even with earplugs.
Almost half of TMS patients get headaches after each session. Taking over-the-counter medications can relieve them.
It is normal to feel facial twitches during the treatment.
Although the risk of having seizures is low, the patient must still keep this side effect in mind.
The patient may also experience minor scalp discomfort, but this often subsides.
TMS is a good alternative treatment for depression
Conventional treatments do not always work for MDD patients. Over time, these patients become treatment-resistant. To help these patients, psychiatrists provide TMS sessions. This type of approach is non-invasive. Patients who complete the sessions experience complete remission. Talking to your psychiatrist will help determine if you qualify for TMS.
Become a new patient today or give us a call: 631-673-3233.